Grocery competition is dwindling in rural America as federal funding to rebuild it is on the chopping block.
If you live in a small town, you probably have fewer grocery stores than you did 30 years ago — and fewer choices inside them.
Independent grocers have disappeared, replaced by big national chains that now decide what’s on the shelves, how much it costs, and who gets to profit.
In 1990, the top four grocery chains controlled just 13 percent of nationwide sales. By 2019, the top four retailers — Walmart, Kroger, Costco, and Ahold Delhaize — controlled 34 percent of U.S. grocery sales, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
That concentration hasn’t gone unnoticed. Just last year, the Federal Trade Commission and nine states sued to block a $25 billion merger between grocery giants Kroger and Albertsons, arguing that the deal would harm both shoppers and workers by reducing competition, increasing prices, and consolidating power into fewer hands. The merger has since unraveled, but only after a court battle and mounting public pressure.
In rural counties, market concentration more than doubled between 1990 and 2019, according to USDA data.
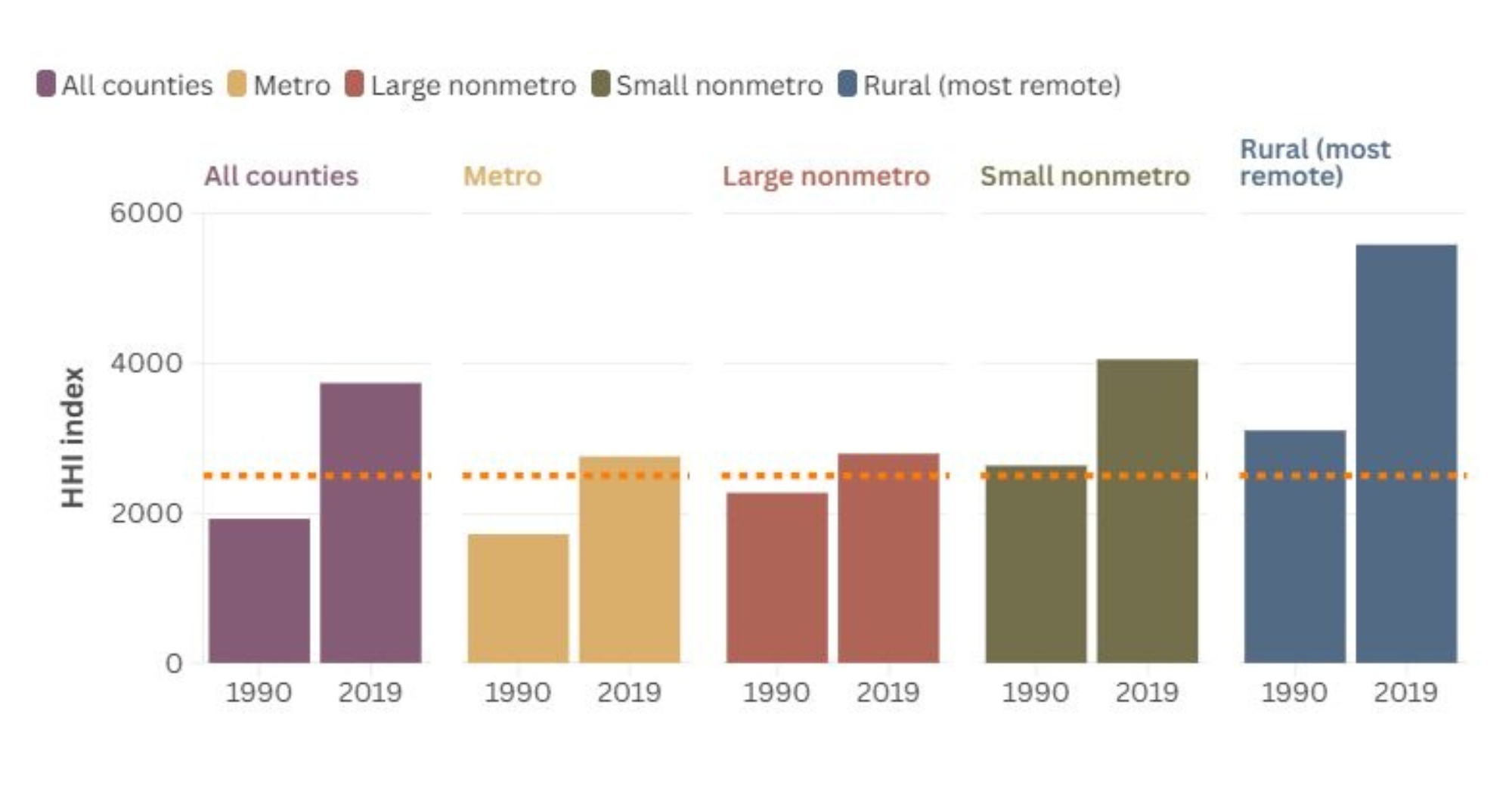
The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) is a tool regulators use to track monopoly risk. A perfectly competitive market might score near 1,000, while a monopoly scores 10,000. The dotted orange line represents the 2,500 HHI threshold used by federal regulators to flag highly concentrated markets.
One way to measure concentration is the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI), a tool used to track monopoly risk. In rural areas, HHI scores jumped from 3,104 to 5,584 — more than twice the threshold where federal antitrust regulators start to worry about competition. According to a 2023 USDA report, the USDA considers anything above 2,500 is considered highly concentrated.
Now that trend may speed up. The White House has proposed nearly $7 billion in USDA budget cuts, including $721 million from Rural Development programs — the ones that help small towns open grocery stores and other local businesses. One program on the chopping block is the Rural Business-Cooperative Service. Loan funding for community facilities and rural businesses would also drop by 45 percent, with no new grant dollars offered.
At the same time, the administration’s “Make America Healthy Again” initiative discusses improving nutrition, but proposes cuts to the very programs that help people buy food, including Women, Infants, and Children, school meal equipment, and farm-to-school efforts.
The bottom line? Rural communities already hit hardest by grocery consolidation are now facing even more roadblocks.
Investigate Midwest is an independent, nonprofit newsroom. Our mission is to serve the public interest by exposing dangerous and costly practices of influential agricultural corporations and institutions through in-depth and data-driven investigative journalism. Visit us online at www.investigatemidwest.org.


